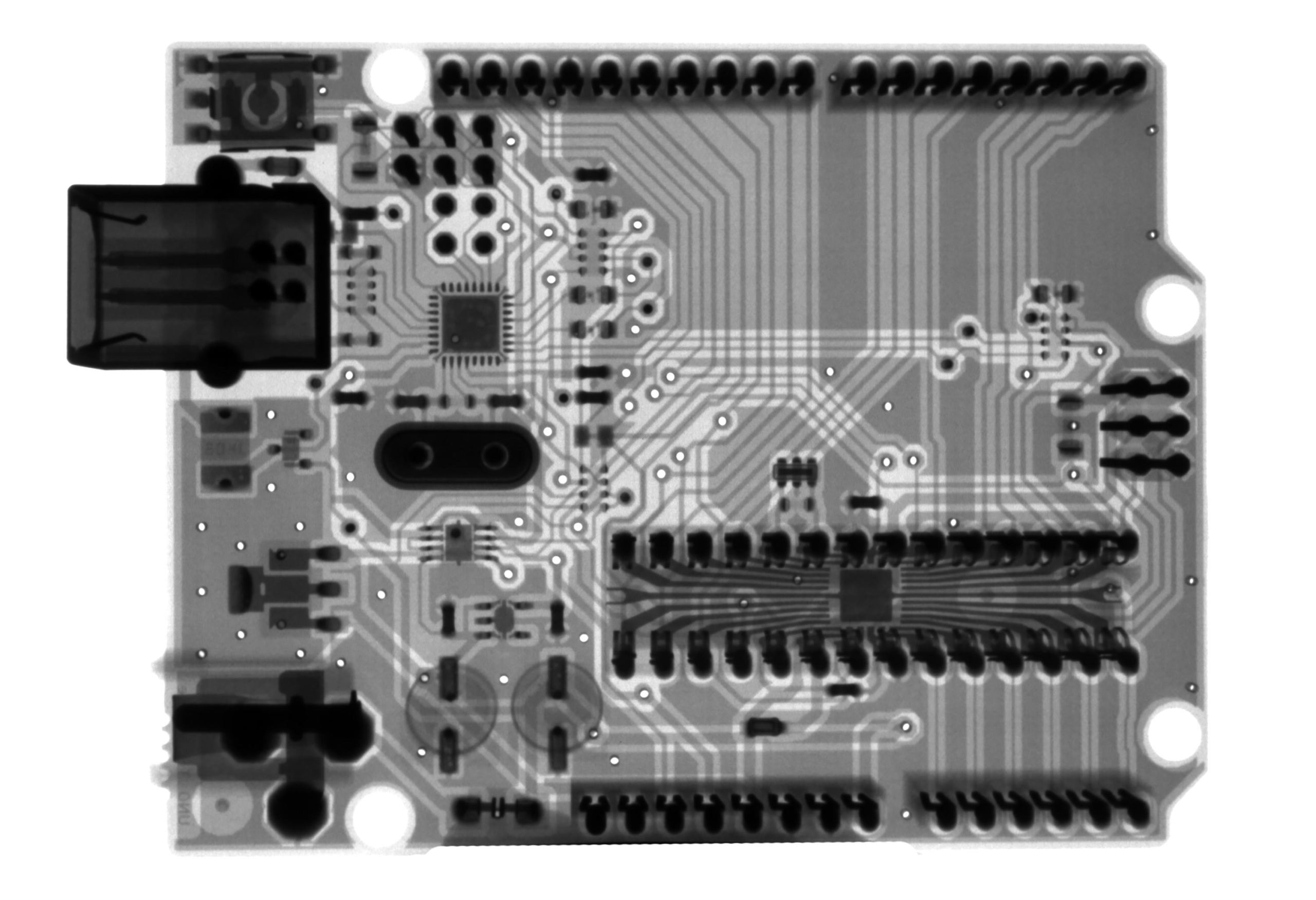
Many different types of materials can be used for a printed circuit board.
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is one or more layers of insulating material with conductive pathways etched into it. A PCB supports mechanically and electrically connecting electronic components using conductive tracks, pads, and other features etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. Printed circuit boards are used in almost all computers, cell phones, and other electronic devices.
The most common substrate material for PCBs is FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate rated at 155°C. However, many other substrate materials are available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The choice of substrate material is often dictated by the application and the required performance of the PCB.
Some common substrate materials used for PCBs include:
FR-4: FR-4 is the most common substrate material for PCBs. It is a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate with a dielectric constant of 4.4 and a thermal conductivity of 0.8 W/mK. FR-4 has excellent dimensional stability and is resistant to most chemicals. It can operate at temperatures up to 155°C.
FR-5: FR-5 is a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate with a dielectric constant of 4.4 and a thermal conductivity of 1.0 W/mK. FR-5 can operate at temperatures up to 175°
What Is Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
The blank printed circuit board material is the base material on which the circuitry is printed.
You may have never given much thought to the printed circuit board (PCB) on your computer or phone, but this humble little board is responsible for a lot. In its simplest form, a PCB is a board made of insulating material (usually fiberglass) with metal tracks. These tracks connect different components on the board and allow them to communicate.
PCBs are used in various electronics, from simple circuits to the most complex computers. They come in all shapes and sizes, and the size and complexity of a PCB are usually determined by the number of components it needs to connect.
The material that a PCB is made from is essential, as it must withstand the heat and stress of being used in an electronic device. The most common material for PCBs is FR4, a fiberglass type. Other materials include polyimide and Teflon.
FR4 is a good choice for PCBs as it is solid, durable, and can withstand high temperatures. It is also relatively easy to work with, essential as PCBs must be manufactured to exact standards.
Polyimide is another popular choice for PCBs, as it has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means that it will not change shape when exposed to heat, making it ideal for use in electronic devices.
Teflon is another common material for PCBs and is often used in high-temperature applications. It has a very low dielectric constant, which means that it does not store electrical charge and is ideal for electronic devices.
The material you choose for your PCB will depend on the application it is used for. For example, FR4 is an excellent all-around choice for PCBs, but if you need a PCB for a high-temperature application, then Teflon may be a better choice.
What Are The Benefits Of Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
The benefits of blank printed circuit board material are that it is easy to work with and has a high degree of accuracy.
There are many benefits to using blank printed circuit board (PCB) material. Some of these benefits include:
1. Increased reliability: Blank PCBs are less likely to fail than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the manufacturing process is more straightforward, and there are fewer potential points of failure.
2. Cost savings: Blank PCBs are typically less expensive than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the manufacturing process is more straightforward, and fewer materials are required.
3. Flexibility: Blank PCBs offer more flexibility than those with pre-printed circuitry. A company can customize the circuitry to meet the application’s specific needs.
4. Increased performance: Blank PCBs often outperform those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the circuitry can be optimized for the specific application.
5. Reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI): Blank PCBs typically emits less electromagnetic interference (EMI) than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the circuitry is not as densely packed, reducing the amount of electromagnetic radiation emitted.
6. Better thermal management: Blank PCBs often have better thermal control than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the circuitry can be designed to dissipate heat more effectively.
7. Increased durability: Blank PCBs are typically more durable than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the manufacturing process is simpler, and there are fewer potential points of failure.
8. Increased service life: Blank PCBs often have a longer service life than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the manufacturing process is more straightforward, with fewer potential points of failure.
9. Increased safety: Blank PCBs are often safer than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the circuitry can be designed to meet stricter safety standards.
10. Environmental benefits: Blank PCBs often have less of an impact on the environment than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the manufacturing process is more straightforward, and fewer toxic chemicals are used.
What Are The Drawbacks Of Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
There are several drawbacks to blank printed circuit board material, including the fact that it is not as durable as other materials and can be challenging to work with.
There are many different types of printed circuit board (PCB) materials on the market, each with its unique properties and applications. While blank PCB material has many benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks.
One of the most significant drawbacks of blank PCB material is its cost. Blank PCBs are typically more expensive than those already populated with components. This is because the manufacturing process is more complex and time-consuming.
Another potential drawback is that blank PCBs can be more challenging to work with. This is because they often require special tools and expertise to assemble correctly. If you are not experienced in working with PCBs, it is best to leave this task to the professionals.
Finally, blank PCBs can also be more susceptible to errors and defects. This is because there are more opportunities for things to go wrong during manufacturing. If you are careful, you may end up with a faulty board that works correctly.
Despite these potential drawbacks, blank PCBs still offer many advantages. They are often more reliable and durable than populated boards and can be custom-designed to meet your specific needs. So if you are looking for a high-quality PCB for your next project, blank material may be the way to go.
How Does Blank Print Circuit Board Material Compare To Other Materials?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the best material for a printed circuit board (PCB) depends on the specific application and requirements of the project.
Printed circuit board (PCB) material is important when choosing the right board for your project. There are a few different types of PCB materials, each with its benefits and drawbacks. Here’s a quick comparison of the most common PCB materials:
FR-4: FR-4 is the most common type of PCB material. It’s a flame-resistant glass-reinforced epoxy laminate with good mechanical strength. As a result, FR-4 is the preferred material for most PCB applications.
FR-2: FR-2 is a lower-cost alternative to FR-4. It’s made of paper-reinforced phenolic resin and is not as flame-resistant as FR-4. As a result, FR-2 is typically only used for lower-power applications.
CEM-1: CEM-1 is a low-cost alternative to FR-4. It’s made of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy and is not as flame-resistant as FR-4. As a result, CEM-1 is typically only used for lower-power applications.
Rogers RO4003C: Rogers RO4003C is a high-performance PCB material. It’s made of Rogers’ proprietary TMMR (Thermally conductive, Microwaveable, Moisture Resistant) laminates and has excellent electrical and mechanical properties. As a result, Rogers RO4003C is the preferred material for high-power and high-frequency applications.
Material selection is just one of the many factors to consider when designing a PCB. Other essential factors include board size, thickness, layer count, and trace width.
What Are The Applications Of Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
Some applications for blank printed circuit board material include making electrical circuits, prototyping electronic devices, and creating printed circuit boards for various devices.
Printed circuit boards are used in various electronic devices, from the most straightforward calculators to the most complex computers. They are used in almost all electronic equipment today.
The primary function of a printed circuit board is to provide mechanical support for the electronic components of the device and to connect those components electrically. The components are usually soldered onto the board.
The circuit board may also contain other components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which are needed for the device’s proper functioning.
The circuit board may also contain particular components, such as integrated circuits (ICs). These are usually more complex devices with many transistors and other electronic components in a small package.
Printed circuit boards are used in various electronic devices, from the most straightforward calculators to the most complex computers. They are used in almost all electronic equipment today.
The primary function of a printed circuit board is to provide mechanical support for the electronic components of the device and to connect those components electrically. The components are usually soldered onto the board.
The circuit board may also contain other components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which are needed for the device’s proper functioning.
The circuit board may also contain unique components, such as integrated circuits (ICs). These are usually more complex devices with many transistors and other electronic components in a small package.
FAQ
What Are The Manufacturing Processes For Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
The manufacturing process for blank printed circuit board material generally includes several steps, such as copper foil lamination, drilling, etching, and solder mask.
What Are The Standards For Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
There are a few standards for blank printed circuit board material, the most common being FR-4. FR-4 is a fire-retardant material rated for operating temperatures up to 105 degrees Celsius. Other common materials include FR-2, FR-3, and FR-5.
What Are The Suppliers Of Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
The suppliers of blank printed circuit board material are the companies that manufacture the raw boards. These companies use various materials to make the boards, including fiberglass, epoxy, and polyimide. The panels are then shipped to the customer, who will finish them by adding the electronic components.
How Do I Design A Circuit Board Using Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
To design a circuit board using blank printed circuit board material, you’ll need to create a circuit diagram that includes all the components you want to include on your board. Once you have your graph, you can use a software program like Eagle to lay out your components on the board. Once your components are laid out, you’ll need to connect them with copper traces. Next, you can use a pen or pencil to draw your paths on the board or a computer-aided design (CAD) program to create them. Finally, you’ll need to add holes for mounting components or connecting to external devices.
If you still have questions about the blank printed circuit board material, please feel free to leave a comment below.
PCB, is a board made of one or more layers of insulating material, with conductive pathways etched into it. A PCB is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive tracks, pads and other features etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. Printed circuit boards are used in almost all computers, cell phones and other electronic devices.
The most common substrate material for PCBs is FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate rated at 155°C. However, there are many other substrate materials available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of substrate material is often dictated by the application and the required performance of the PCB.
Some common substrate materials used for PCBs include:
FR-4: FR-4 is the most common substrate material for PCBs. It is a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate with a dielectric constant of 4.4 and a thermal conductivity of 0.8 W/mK. FR-4 has excellent dimensional stability and is resistant to most chemicals. It can operate at temperatures up to 155°C.
FR-5: FR-5 is a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate with a dielectric constant of 4.4 and a thermal conductivity of 1.0 W/mK. FR-5 can operate at temperatures up to 175°
What Is Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
The blank printed circuit board material is the base material that the circuitry is printed on.
You may have never given much thought to the printed circuit board (PCB) that is in your computer or phone, but this humble little board is responsible for a lot. In its simplest form, a PCB is a board made of insulating material (usually fiberglass) with metal tracks. These tracks connect different components on the board together and allow them to communicate with each other.
PCBs are used in a wide range of electronics, from simple circuits to the most complex computers. They come in all shapes and sizes, and the size and complexity of a PCB is usually determined by the number of components it needs to connect.
The material that a PCB is made from is important, as it needs to be able to withstand the heat and stress of being used in an electronic device. The most common material for PCBs is FR4, which is a type of fiberglass. Other materials include polyimide and Teflon.
FR4 is a good choice for PCBs as it is strong and durable, and can withstand high temperatures. It is also relatively easy to work with, which is important as PCBs need to be manufactured to very precise standards.
Polyimide is another popular choice for PCBs, as it has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means that it will not change shape when exposed to heat, making it ideal for use in electronic devices.
Teflon is another common material for PCBs, and is often used in high-temperature applications. It has a very low dielectric constant, which means that it does not store electrical charge and is therefore ideal for use in electronic devices.
The material that you choose for your PCB will depend on the application it is being used for. In general, FR4 is a good all-round choice for PCBs, but if you need a PCB for a high-temperature application, then Teflon may be a better choice.
What Are The Benefits Of Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
The benefits of blank printed circuit board material are that it is easy to work with and has a high degree of accuracy.
There are many benefits to using blank printed circuit board (PCB) material. Some of these benefits include:
1. Increased reliability: Blank PCBs are less likely to fail than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the manufacturing process is simpler and there are fewer potential points of failure.
2. Cost savings: Blank PCBs are typically less expensive than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the manufacturing process is simpler and there are fewer materials required.
3. Flexibility: Blank PCBs offer more flexibility than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the circuitry can be customized to meet the specific needs of the application.
4. Increased performance: Blank PCBs often outperform those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the circuitry can be optimized for the specific application.
5. Reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI): Blank PCBs typically emit less electromagnetic interference (EMI) than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the circuitry is not as densely packed, which reduces the amount of electromagnetic radiation that is emitted.
6. Better thermal management: Blank PCBs often have better thermal management than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the circuitry can be designed to dissipate heat more effectively.
7. Increased durability: Blank PCBs are typically more durable than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the manufacturing process is simpler and there are fewer potential points of failure.
8. Increased service life: Blank PCBs often have a longer service life than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the manufacturing process is simpler and there are fewer potential points of failure.
9. Increased safety: Blank PCBs are often safer than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the circuitry can be designed to meet stricter safety standards.
10. Environmental benefits: Blank PCBs often have less of an impact on the environment than those with pre-printed circuitry. This is because the manufacturing process is simpler and there are fewer toxic chemicals used.
What Are The Drawbacks Of Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
There are several drawbacks to blank printed circuit board material, including the fact that it is not as durable as other materials, and it can be difficult to work with.
There are many different types of printed circuit board (PCB) materials on the market, each with its own unique set of properties and applications. While blank PCB material has many benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider.
One of the biggest drawbacks of blank PCB material is its cost. Blank PCBs are typically more expensive than those that are already populated with components. This is because the manufacturing process is more complex and time-consuming.
Another potential drawback is that blank PCBs can be more difficult to work with. This is because they often require special tools and expertise to properly assemble. If you are not experienced in working with PCBs, it is best to leave this task to the professionals.
Finally, blank PCBs can also be more susceptible to errors and defects. This is because there are more opportunities for things to go wrong during the manufacturing process. If you are not careful, you may end up with a faulty board that does not work correctly.
Despite these potential drawbacks, blank PCBs still offer many advantages. They are often more reliable and durable than populated boards, and they can be custom-designed to meet your specific needs. If you are looking for a high-quality PCB for your next project, blank material may be the way to go.
How Does Blank Printed Circuit Board Material Compare To Other Materials?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the best material for a printed circuit board (PCB) depends on the specific application and requirements of the project.
Printed circuit board (PCB) material is an important factor to consider when choosing the right board for your project. There are a few different types of PCB materials, each with their own benefits and drawbacks. Here’s a quick comparison of the most common PCB materials:
FR-4: FR-4 is the most common type of PCB material. It’s a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate that’s flame-resistant and has good mechanical strength. FR-4 is the preferred material for most PCB applications.
FR-2: FR-2 is a lower-cost alternative to FR-4. It’s made of paper-reinforced phenolic resin and is not as flame-resistant as FR-4. FR-2 is typically only used for lower-power applications.
CEM-1: CEM-1 is a low-cost alternative to FR-4. It’s made of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy and is not as flame-resistant as FR-4. CEM-1 is typically only used for lower-power applications.
Rogers RO4003C: Rogers RO4003C is a high-performance PCB material. It’s made of Rogers’ proprietary TMMR (Thermally conductive, Microwaveable, Moisture Resistant) laminates and has excellent electrical and mechanical properties. Rogers RO4003C is the preferred material for high-power and high-frequency applications.
Material selection is just one of the many factors to consider when designing a PCB. Other important factors include board size, thickness, layer count, and trace width.
What Are The Applications Of Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
Some applications for blank printed circuit board material include making electrical circuits, prototyping electronic devices, and creating printed circuit boards for use in a variety of devices.
Printed circuit boards are used in a wide variety of electronic devices, from the simplest calculators to the most complex computers. They are used in almost all electronic equipment today.
The basic function of a printed circuit board is to provide a mechanical support for the electronic components of the device and to connect those components electrically. The components are usually soldered onto the board.
The circuit board may also contain other components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which are needed for the proper functioning of the device.
In some cases, the circuit board may also contain special components, such as integrated circuits (ICs). These are usually more complex devices that contain a large number of transistors and other electronic components in a small package.
Printed circuit boards are used in a wide variety of electronic devices, from the simplest calculators to the most complex computers. They are used in almost all electronic equipment today.
The basic function of a printed circuit board is to provide a mechanical support for the electronic components of the device and to connect those components electrically. The components are usually soldered onto the board.
The circuit board may also contain other components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which are needed for the proper functioning of the device.
In some cases, the circuit board may also contain special components, such as integrated circuits (ICs). These are usually more complex devices that contain a large number of transistors and other electronic components in a small package.
FAQ
What Are The Manufacturing Processes For Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
What Are The Standards For Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
What Are The Suppliers Of Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
How Do I Design A Circuit Board Using Blank Printed Circuit Board Material?
If you still have questions about the blank printed circuit board material, please feel free to leave a comment below.
Author
-
I'm Shahrear, a Designer Lead who loves electronics. Since 2003, I’ve been traveling and living all over the world. I love breaking down complex concepts in electronics and presenting them to others in an approachable way. I think that the language used in most books about electronics is hard for people who don't already know about electronics to understand. I want that to change. So, I've started blog where I talk about everything on electronics for people who are just starting out.
View all posts